Assignment 9 (Part 2): Follow the thread
Due Wednesday, April 12th, before midnight
The goals for this assignment are:
-
Implement multi-thread algorithms using the pthread library
-
Use mutex and barrier to coordinate between different threads
Update your repository
Do a fetch upstream to obtain the basecode for this assignment.
Using the command line
-
Open terminal and change your current directory to your assignment repository.
-
Run the command
git fetch upstream -
Run the command
git merge upstream/master
Your repository should now contain a new folder named A09.
The fetch and merge commands update your repository with any changes from the original.
1. Buddhabrot
In the file, buddhabrot.c, compute a program that outputs a PPM image of
the Buddhabrot using multiple threads.
The Buddhabrot visualizes the trajectory of each point (x,y) as it escapes the mandelbrot set. The color of each pixel represents the probability of a point (x,y) visiting it while we calculate whether or not it belongs to the mandelbrot set.
Computing the Buddhabrot set requires three steps:
-
First, determine whether a point is in the mandelbrot set. Recall the points within the set remain less than 2*2 and are given a black color. Store whether a point escapes as a boolean in its own 2D array.
-
Second, for the points that do escape, you must update counts for each (x,y) coordinate visited. Store these counts in its own 2D array. Also keep track of the max count for any pixel.
-
Third, you must turn the counts from step 2 into a color. The final colors should be written to a 2D array of ppm_pixel (either flat or an array of arrays) and then written.
Each of the above steps can be parallelized using threads. The second step will require a mutex to ensure that the counts are set correctly. Below are suggested algorithms for computing each step.
Step 1: Determine mandelbrot set membership
for each row in the image
for each col in the image
xfrac = row / image_size
yfrac = col / image_size
x0 = xmin + xfrac * (xmax - xmin)
y0 = ymin + yfrac * (ymax - ymin)
x = 0
y = 0
iter = 0
while (iter < MAX && x*x + y*y < 2*2)
xtmp = x*x - y*y + x0
y = 2*x*y + y0
x = xtmp
iter++
if (iter < MAX) // escaped
set membership at (row,col) to false
else
set membership at (row,col) to trueStep 2: Compute visited counts
for each row in the image
for each col in the image
if (row,col) belongs to the mandelbrot set, continue
xfrac = row / image_size
yfrac = col / image_size
x0 = xmin + xfrac * (xmax - xmin)
y0 = ymin + yfrac * (ymax - ymin)
x = 0
y = 0
while (x*x + y*y < 2*2)
xtmp = x*x - y*y + x0
y = 2*x*y + y0
x = xtmp
yrow = round(size * (y - ymin)/(ymax - ymin))
xcol = round(size * (x - xmin)/(xmax - xmin))
if (yrow < 0 || yrow >= size) continue; // out of range
if (xcol < 0 || xcol >= size) continue; // out of range
increment count at (yrow, xcol)
update max countStep 3: Compute colors
gamma = 0.681
factor = 1.0/gamma
for each row in the image
for each col in the image
value = 0
if counts at (row,col) are greater than zero
value = log(counts[row][col]) / log(max_count)
value = pow(value, factor)
color.red = value * 255
color.green = value * 255
color.blue = value * 255
write color to image at location (row,col)Each thread should compute the three steps on a quadrant of the image. Below is a suggested outline for your thread’s start routine.
void * start(void* data) {
// perform step 1
// perform step 2
// use a thread barrier to wait for all threads to finish steps 1 and 2
// perform step 3
}$ ./buddhabrot
Generating buddhabrot with size 480x480
Num processes = 4
X range = [-2.5000,1.0000]
Y range = [-1.1200,1.1200]
Generating mandelbrot with size 480x480
X range = [-2.0000,1.0000]
Y range = [-1.1200,1.1200]
Thread 140583141971712) sub-image block: cols (0, 240) to rows (0,240)
Thread 140583133579008) sub-image block: cols (240, 480) to rows (0,240)
Thread 140583125186304) sub-image block: cols (0, 240) to rows (240,480)
Thread 140583116793600) sub-image block: cols (240, 480) to rows (240,480)
Thread 140583141971712) finished
Thread 140583133579008) finished
Thread 140583125186304) finished
Thread 140583116793600) finished
Computed buddhabrot set (480x480) in 0.123721 seconds
Writing file: buddhabrot-480-1650141479.ppm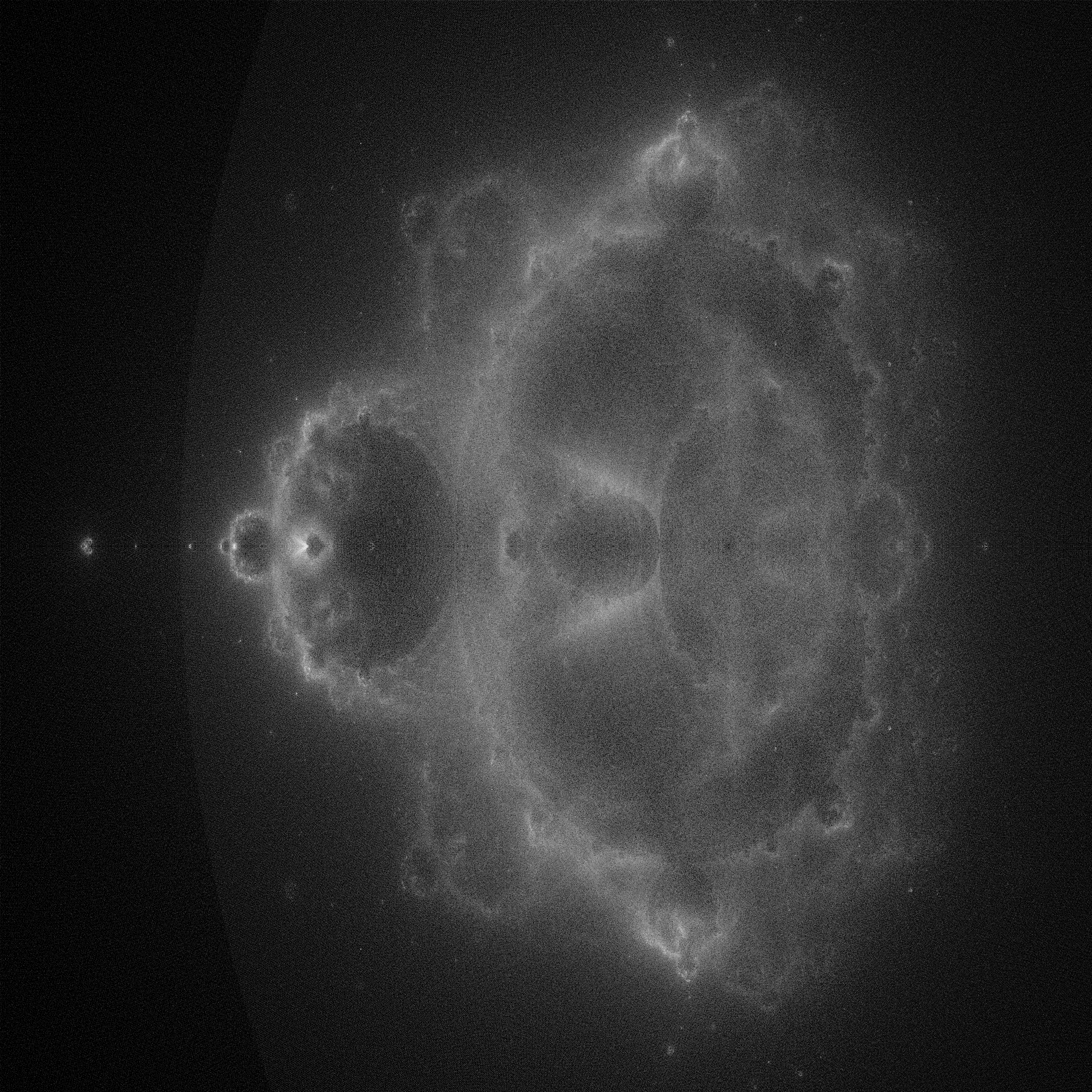
Requirements and hints:
-
You can re-use your PPM and mandelbrot functions from A09. You should re-use your implementation for read/write PPM as well.
-
Each thread should run all three steps on a quadrant of the image.
-
You will need a
pthread_barrier_tto wait for all counts to be computed before computing the colors -
Notice that the range of x and y might need to be larger to see the probability distribution
-
Use mutex to compute the counts
-
You should output the number of seconds needed to compute the image. Use this class example, matrix.c for an example.
-
Your output filename should have the format
buddhabrot-<size>-<timestamp>.ppm. The timestamp can be obtained by callingtime(0). -
You may use global variables for this program.
| Above, we compute a greyscale mandelbrot. To add colors, compute counts for the red, green, and blue channels separately, using different values for maxIterations in each. For example the following image used 5000 for red, 500 for green, and 50 for blue. |

| Other chaotic sets can be visualized in the same way as the Buddhabrot. To see more, read about Fractal Frames. |
2. Submit your work
Submit both your code and images.
1) Push your code work to github
$ git status
$ git add .
$ git status
$ git commit -m "assignment complete"
$ git status
$ git push
$ git status